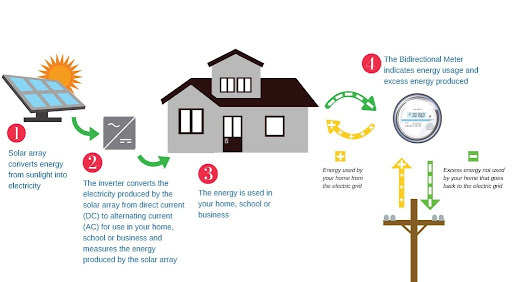
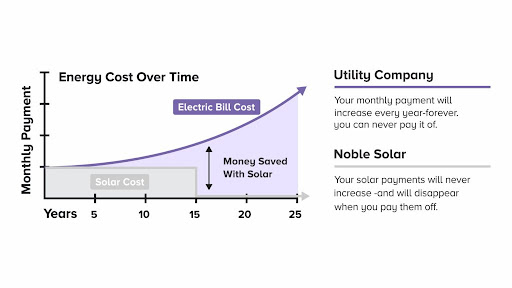
Hydroelectric power has long been hailed as a clean and renewable energy source, providing electricity to millions of people worldwide. It harnesses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity and has been a staple of the global energy mix for decades. However, like any energy source, hydroelectric power comes with its own set of costs, both in the present and the future. Let’s try to understand the true costs of hydroelectric power, examining the economic, environmental, and social factors that shape its sustainability and impact also while exploring sustainable alternatives with Solar Resource.
The Basics of Hydroelectric Power
Before we dive into the costs, let’s understand how hydroelectric power works:
Hydroelectric Power Generation Process
Hydroelectric power generation involves several key steps:
Dam Construction
A dam is built across a river to create a reservoir, storing a large amount of water. The construction of a dam can cost billions of dollars, depending on its size and complexity. For instance, the Three Gorges Dam in China, one of the world’s largest, had an estimated cost of over $28 billion.

Water Release
Water is released from the reservoir, flowing through turbines in the dam. The flow rate can be adjusted to meet electricity demand, providing flexibility in electricity production.
Turbine Rotation
The flowing water causes the turbines to rotate, converting kinetic energy into mechanical energy. This rotational energy is crucial for electricity generation.
Electricity Generation
The mechanical energy drives generators, producing electricity that is sent to the grid for distribution. Hydroelectric power accounts for approximately 16% of global electricity production, with an installed capacity of around 1,300 GW.
Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants
There are two main types of hydroelectric power plants:
Conventional Dams
Large dams are constructed, creating reservoirs for power generation. These dams can store vast quantities of water, such as the Hoover Dam in the United States, which holds around 28 million acre-feet of water. However, the construction of such dams can displace communities and have significant environmental impacts.
Run-of-River Plants
These plants do not require large dams and generate electricity directly from the flowing river. They are considered more environmentally friendly, as they typically have smaller footprints and less impact on aquatic ecosystems. Smaller run-of-river plants can have construction costs ranging from $1 million to $20 million per MW of installed capacity.

The Current Costs of Hydroelectric Power
Economic Costs
Hydroelectric power has some significant economic advantages:
Low Operating Costs
Once dams are constructed, operating costs are relatively low, as the fuel source (water) is free. Annual maintenance costs for hydroelectric plants typically range from $5,000 to $20,000 per MW of installed capacity.
Long Lifespan
Hydroelectric plants have a long lifespan, often exceeding 50 years, providing a stable source of energy. The refurbishment of older plants can cost between $100 and $500 per kW of capacity, extending their operational life.
Job Creation
The construction and maintenance of hydroelectric plants create jobs in the local economy. A large hydroelectric project can employ thousands of people during the construction phase and support hundreds of jobs during operation.
Environmental Costs
While hydroelectric power is considered a clean energy source, it is not without environmental consequences:
Habitat Disruption
The creation of large reservoirs can displace wildlife and alter local ecosystems. For instance, the filling of the Kariba Dam reservoir in Africa led to the displacement of approximately 57,000 people and impacted wildlife, including fish populations.

Methane Emissions
The decomposition of organic matter in reservoirs can produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Some estimates suggest that hydroelectric reservoirs emit as much as 104 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year due to methane emissions. Environment conservatives have started urging for a greener and more sustainable way of generating electricity.
Sediment Trapping
Dams can trap sediment, affecting downstream river ecosystems and water quality. The cost of sediment management, including dredging operations, can run into millions of dollars annually for larger dams.
Social Costs
Hydroelectric power also has social implications:
Displacement of Communities
Building dams often involves the relocation of communities, impacting their way of life. The cost of compensating and resettling displaced communities can be substantial, often reaching hundreds of millions of dollars for large projects. Instead of benefiting the local communities, these projects often lead to their complete dismantling.
Indigenous Rights
Many hydroelectric projects encroach on lands traditionally occupied by indigenous peoples, leading to conflicts over land rights. Respecting and addressing indigenous rights can require additional investments in consultation and collaboration, driving up project costs.

The Future Costs of Hydroelectric Power
As we look to the future, it’s crucial to consider how the costs of hydroelectric power may evolve:
Economic Considerations
Aging Infrastructure
Many existing dams are reaching the end of their operational life, requiring expensive repairs or decommissioning. The cost of dam removal or extensive rehabilitation can be several million dollars per dam.
Climate Change
Changing weather patterns and increased droughts can reduce water availability, affecting power generation. Hydroelectric plants may face decreased capacity and increased operational uncertainties due to climate change impacts.
Environmental Sustainability
Greening Hydroelectricity
Innovative technologies, such as fish-friendly turbines and sediment management techniques, aim to mitigate the environmental impact of hydroelectric power. Investing in these technologies can add to the upfront costs of hydroelectric projects.
Decommissioning and Dam Removal
Some older dams may be removed to restore natural river flows and ecosystems. The cost of decommissioning and the potential benefits in terms of environmental restoration will be critical considerations in the future. The estimated cost of dam removal can range from $10 million to $100 million per dam, depending on its size and location.

Social Responsibility
Indigenous Rights and Collaboration
Recognizing indigenous rights and involving communities in decision-making can lead to more sustainable and socially responsible hydroelectric projects. However, these efforts may require additional investments in community engagement and mitigation measures, increasing project costs.
Public Perception
Public opinion is increasingly shaping energy policies, with concerns about environmental and social impacts playing a crucial role. Energy companies and policymakers must take public sentiment into account when planning and implementing hydroelectric projects. Public support for such projects can significantly impact their feasibility.
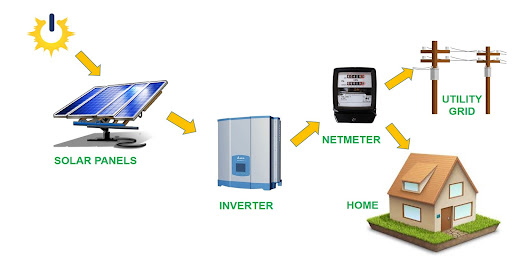
Solar Power: A Sustainable Alternative to Hydroelectric Energy
In the quest for sustainable energy sources, it’s essential to consider alternatives to hydroelectric power that can complement our energy mix. Solar power emerges as a promising and environmentally friendly solution. Solar panels harness the abundant energy from the sun, converting it into electricity without the need for large dams or significant environmental disruptions.

Moreover, solar power offers scalability, making it accessible to both homeowners and large-scale businesses. With falling costs and technological advancements, solar power has become increasingly affordable and efficient, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. As we weigh the true costs of hydroelectric power, exploring alternatives like solar energy can play a crucial role in building a more diversified, sustainable, and resilient energy future. Contact Solar Resource today to get a quote for a solar panel installation that best fits your needs.
Need of the hour
Hydroelectric power is a valuable source of renewable energy with both benefits and costs. Understanding these costs is essential for making informed decisions about our energy future. As we strive for a more sustainable and equitable world, it’s crucial to balance the advantages of hydroelectric power with the need to minimize its economic, environmental, and social costs also while figuring out long-term alternatives like solar energy. Only through careful planning, innovation, and responsible practices can we make our world environment-friendly and sustainable.